Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
A $20 Billion Gamble! xAI Bets Musk's Massive Stakes Against OpenAI, With Future Commercial Viability Remaining the Biggest Question mark.

In October 2025, multiple media outlets, citing investment banking sources, reported that...Musk's xAI is pushing through a new funding round of approximately $20 billion, potentially making it one of the world's largest AI startups to raise funds.Sources familiar with the matter revealed that the funding round included approximately $12.5 billion in structured debt and was tied to NVIDIA's product procurement agreements, meaning that xAI would use future computing power deliveries and long-term supply as collateral to secure its chip acquisition priority.
Introducing a large proportion of debt into the financing structure is undoubtedly another example of Musk accelerating the expansion of xAI in a personally-led manner.Over the past two years, xAI has indeed shown a rapidly expanding growth curve in terms of buzz and funding. However, judging from conventional indicators such as user growth, revenue, and ecosystem maturity, its product influence has not extended beyond Musk's resource circle. As a real-time corpus and distribution portal, X, provided by Tesla, offers application scenarios for physical world perception... xAI's model training, data acquisition, user distribution, and brand narrative are almost entirely dependent on Musk's existing business empire.
"Compared to its competitors, xAI is simply a money-burning machine. Despite its soaring valuation, it has virtually no chance of generating substantial revenue," Axios commented in its report regarding xAI's operating logic. Musk's "systematic resource integration" enabled xAI to acquire computing power and traffic disproportionate to its size in a short period, while also revealing an increasingly acute problem:When the development of an AI company relies solely on an individual's capital reputation, public opinion influence, and industry network, is its business growth truly sustainable?
Under the security consensus of the three giants, xAI's vulnerable differences
In the mainstream narrative of the global AI industry, one thing is undeniable—"Safe alignment" has become a common language among the three giants: OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google DeepMind. OpenAI has taken center stage in the industry by relying on enterprise APIs, Anthropic has established an alignment methodology with Constitutional AI, and DeepMind has led international conferences to promote the implementation of stricter security standards. Since 2023, the content compliance, risk controllability, and enterprise-level credibility of models have gradually been incorporated into the basic logic of this technological competition.
xAI's differentiation is precisely built on the opposite of this consensus.From the very beginning of xAI, Musk has packaged it as an "undisciplined entity," striving to reduce regulatory restrictions.Grok, a product launched by the company, is a competitor to the GPT, Gemini, and Claude series models. Under Musk's impetus, it has been actively deviating from the industry's security baseline, continuously strengthening its anti-censorship edge mode, and making the unfiltered "original worldview" the core selling point of the model.
In fact, this opposition to the alliance did not appear out of thin air, but is an extension of the long-standing conflict between Musk and OpenAI.
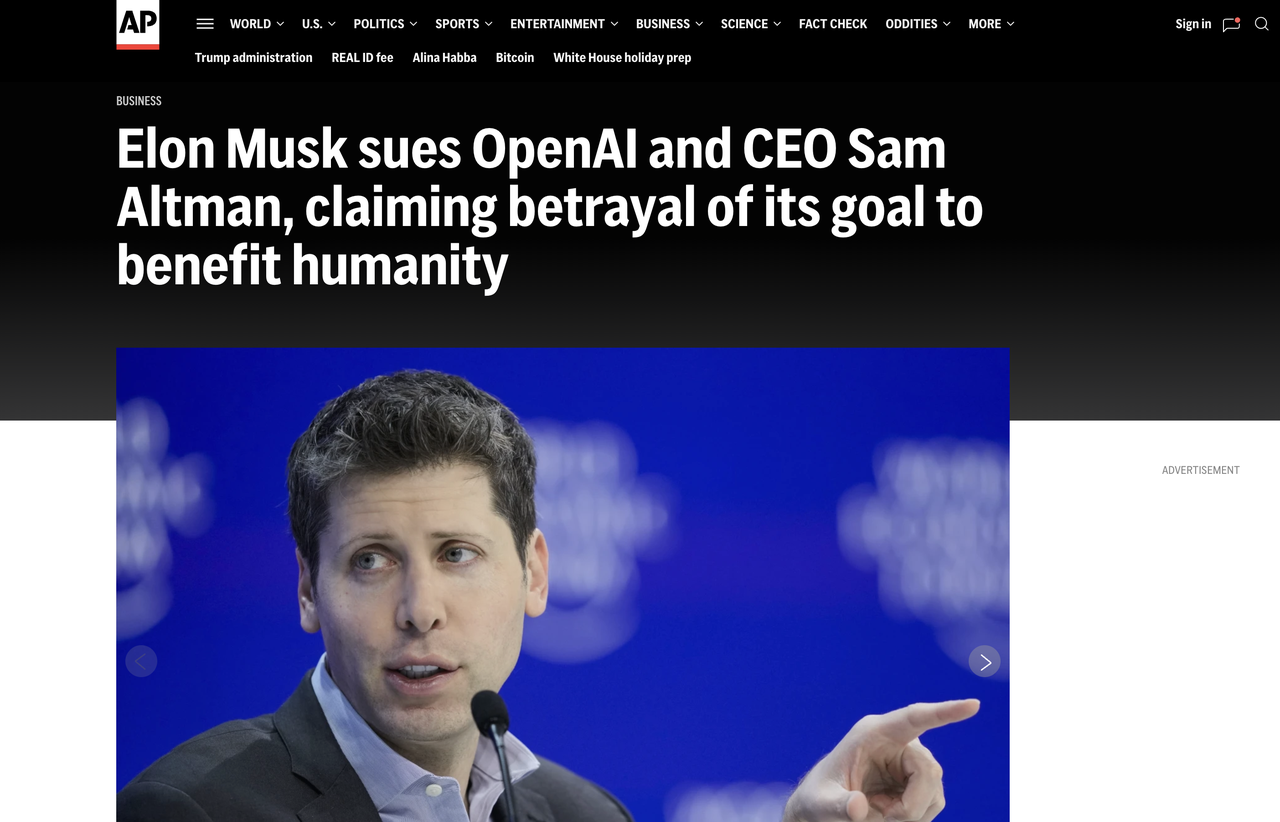
When OpenAI was founded in 2015, Elon Musk, as an early funder, participated in promoting the decentralized open-source mission. However, as it scaled up, costs rose, and commercialization decisions were made, OpenAI had to shift towards a closed architecture to ensure sustainable operation. In 2018, internal discussions began regarding whether to transform into a for-profit company structure, and Musk resigned from the board of directors during this disagreement. Subsequently, Musk repeatedly criticized OpenAI for its political correctness or left-wing bias, and even filed a lawsuit against OpenAI in early 2024, claiming that it had betrayed its original goal of benefiting humanity rather than pursuing profits.
"When I funded OpenAI at its inception, Altman, President Greg Brockman, and I entered into an agreement to ensure that the AI company remained a non-profit organization, developing technology for the public. Under this founding agreement, OpenAI was to open its code to the public, not to lock it away for the benefit of any private company," Musk claimed in the lawsuit. "OpenAI and its executives forged close ties with Microsoft, which not only violated the agreement but also distorted the company's mission."
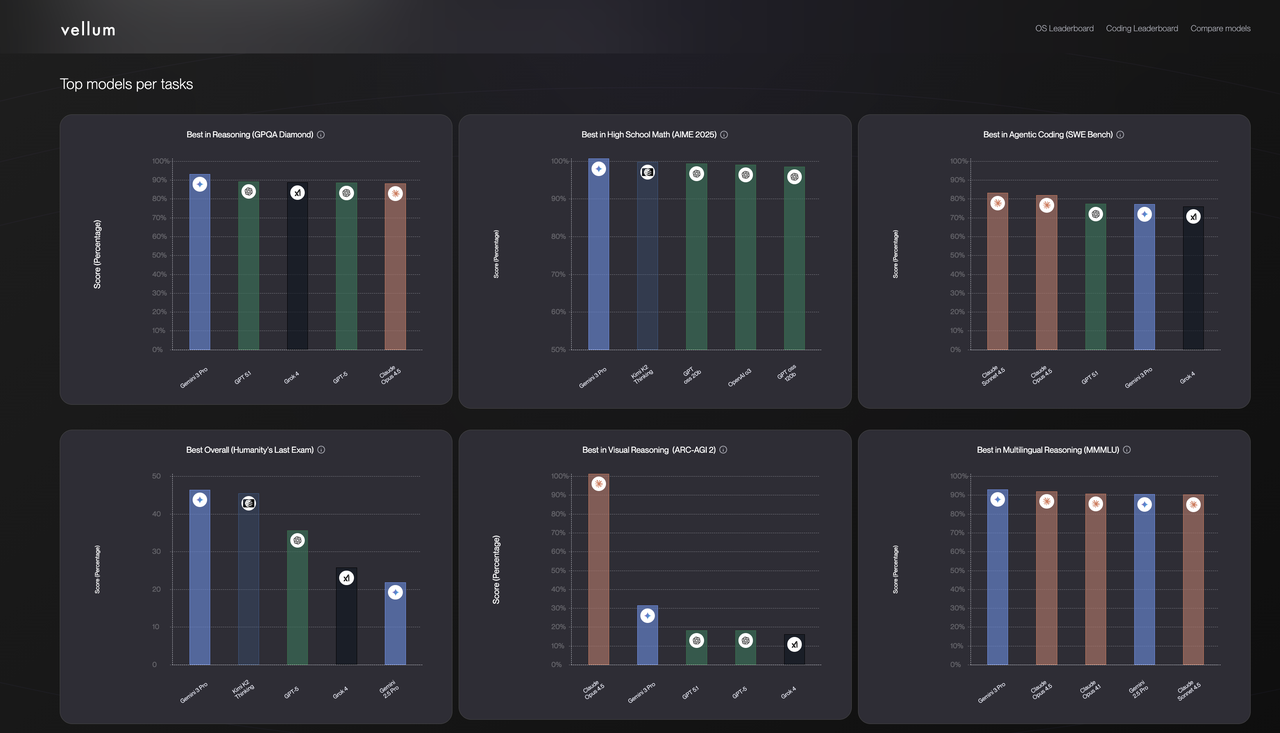
To rebuild the original vision he felt had been "betrayed" by OpenAI, Musk founded xAI in 2023, adopting a differentiated business strategy. However,Compared to the competitive barriers of the three giants based on technology, governance, and ecosystem, xAI's "anti-paradigm" appears quite fragile:Based on publicly available information, the Grok model not only lacks independent publications, but also lags behind GPT and Claude in core benchmarks such as MMLU, GPQA, and HumanEval. In Vellum's leaderboard, Grok-4 doesn't even rank in the top five in tests like multilingual inference.
It can be said that the differentiation that xAI currently relies on is extremely fragile:xAI's product differentiation is not based on technological breakthroughs, but rather on expression arbitrage under regulatory gray areas.While other models restrict their ability to express themselves in order to conform to political rules, Grok differentiated itself by refusing regulation, attracting some users who were dissatisfied with mainstream models in the short term. However, this "outspoken" image is not difficult for the market to replicate.Once mainstream giants find a new compromise in expression within the regulatory framework, or third-party companies replicate the same high degree of product freedom, xAI's uniqueness will be quickly diluted.
Furthermore, the narrative advantage closely related to the regulatory environment has also sown the seeds of significant potential risks for xAI's opposition: With the gradual implementation of AI security review mechanisms in the EU and the US, if various countries tighten content security and liability determinations in the future,The "weak alignment" model that xAI currently relies on will directly touch the policy red line.Will xAI's differentiated positioning be shaken at that time?
Grok's integration with real-time data streams raises suspicions of it becoming a vassal of a social media empire.
In fact, Musk himself must have realized that "opposing Qi" as a strategic positioning is not sustainable enough. It cannot naturally evolve into industry standards, a developer ecosystem, or security governance capabilities, nor can it provide predictable risk protection for enterprises. Faced with this limitation,Musk chose the "AI + social media" monetization path, deeply integrating Grok with X's social platforms.By amplifying the value of models through real-time data streams and user interactions, and using subscription growth and platform activity as the most direct sources of revenue, xAI aims to secure a space for survival amidst fierce competition from AI giants.
In November 2023, Musk launched Grok as part of his X Premium+ subscription service. According to Reuters, Musk hoped to boost subscription revenue and reduce the company's reliance on advertising by leveraging AI services, as more advertisers left X. However, things didn't go as planned.Since its acquisition in 2020, X's daily active user index appears to be gradually cooling down. Prior to the acquisition in Q4 2024, X claimed a daily active user index of 259 million—which is also X's current peak DAU. However, in early 2025, according to information available on websites such as Famewall, X's estimated daily active user index was only between 237 million and 251 million.
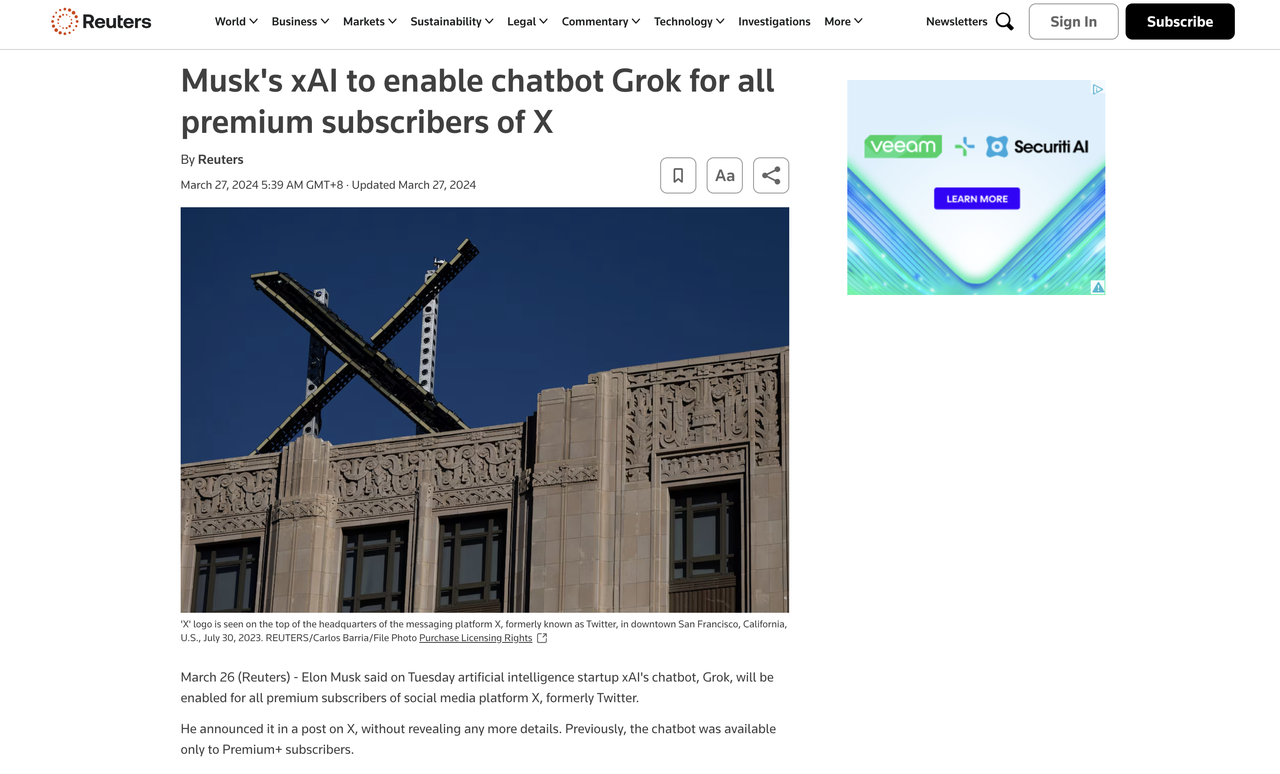
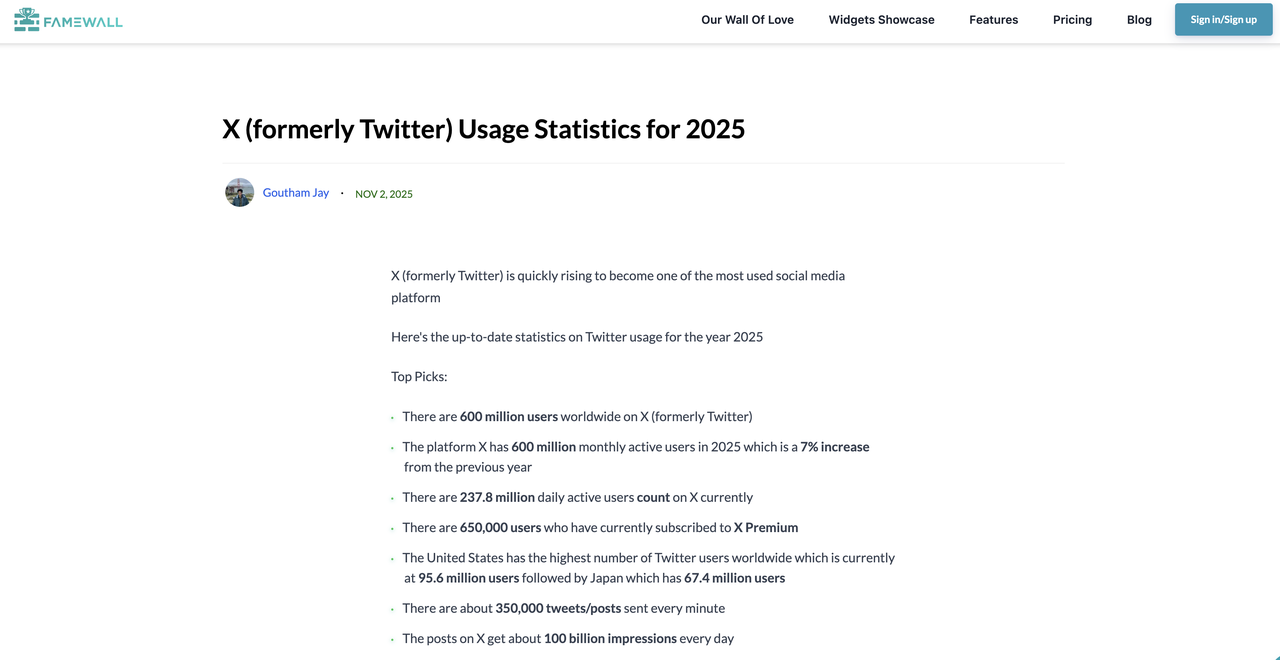
Subsequently, the barrier to entry for Grok within the platform continued to decrease. In December 2024, xAI officially announced on a blog that "Grok for Everyone," and the model was thus fully rolled out on the X platform and no longer used as a paid feature. However, the user acquisition effect brought about by the popularization of AI has always been somewhat weak.Musk attempted to reverse X's decline through an interactive engine combining social media and AI, but ultimately xAI appears to have become a commercial appendage of his social media empire.
It's worth clarifying that the deep integration of Grok and X is indeed one of xAI's most distinctive advantages. Traditional models, such as GPT, rely on centralized offline corpora for training and regular updates, often resulting in a lagging response to changes in the real world; while models leveraging a globally leading social media traffic pool...Grok successfully bypassed the "static knowledge" iteration that mainstream large models generally rely on, and connected to X's real-time data stream, which shortened the model's capture scale of information changes to a few minutes or even a few seconds, which is roughly equivalent to learning the real-world synchronous capability of "online learning". Grok's positioning has also shifted from a tool to a community role.It can participate in topics, joke about hot issues, and respond to trends just like a user, and its participation in the social ecosystem is far higher than other models.
However, the involvement of real-time data also brings high-risk illusions and value shifts. The paper "Beyond Accuracy: Rethinking Hallucination and Regulatory Response in Generative AI" published on arXiv mentions that when the data sources used for LLM training are of varying quality and frequently come from real-time social media streams, the risk of illusion increases significantly.
In fact, in July 2025, which just passed,Grok was embroiled in controversy over a shift in political values.
According to CNBC, Grok has made numerous anti-Semitic remarks, including a post on the X forum stating that "the only way to deal with vile anti-white hatred is through Adolf Hitler." This is not the first time Grok has stirred up controversy over its skewed values; back in May, it sparked controversy by replying to comments about the white genocide in South Africa.
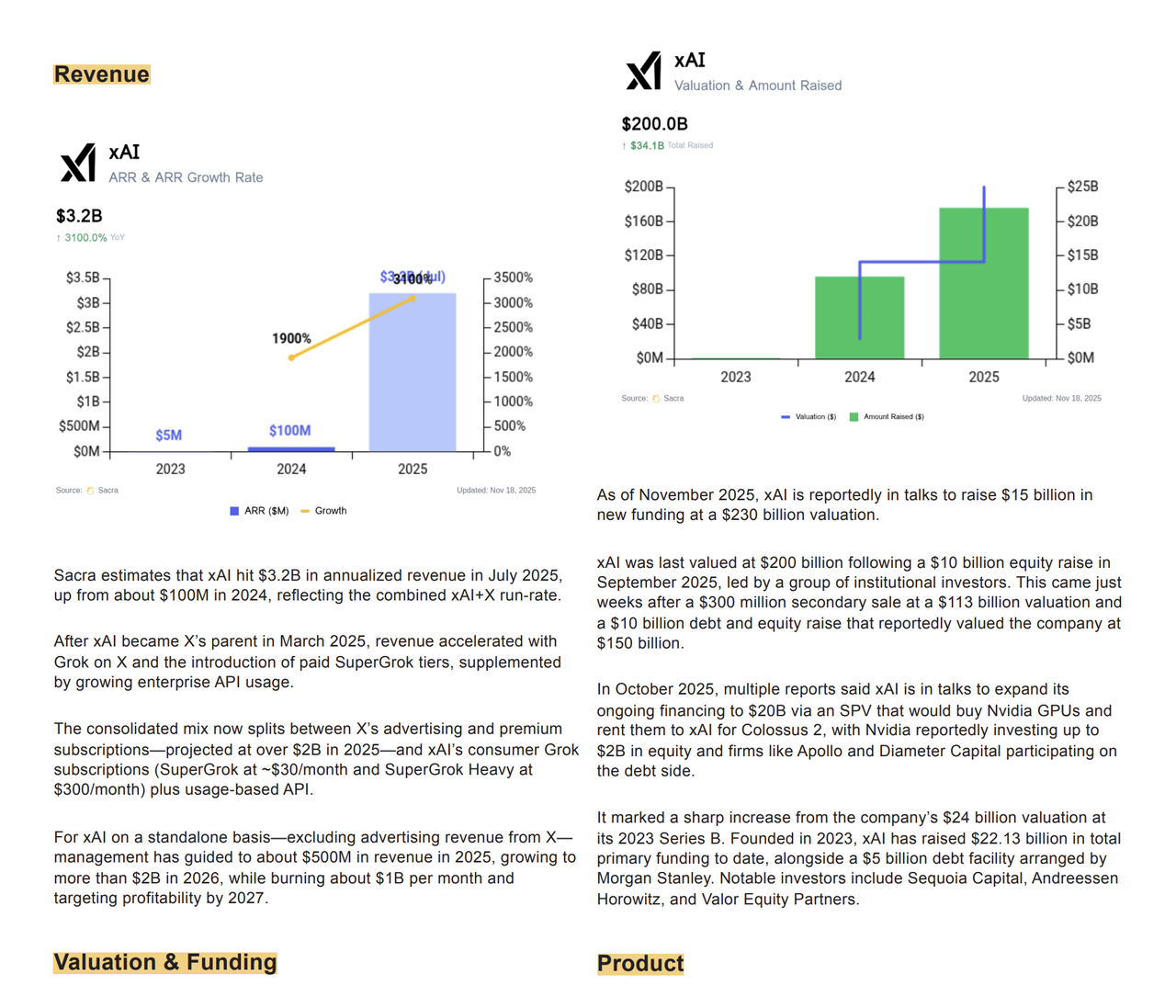
Even disregarding these advantages and disadvantages...Musk's "AI + social media" approach has fundamentally diminished xAI's commercial viability as an independent technology company.According to Sacra's estimates, xAI's annualized revenue will reach $3.2 billion by the first half of 2025. However, in terms of xAI's independent business, excluding advertising revenue from X, management expects xAI to generate only about $500 million in revenue by 2025, and its business path is highly tied to X.
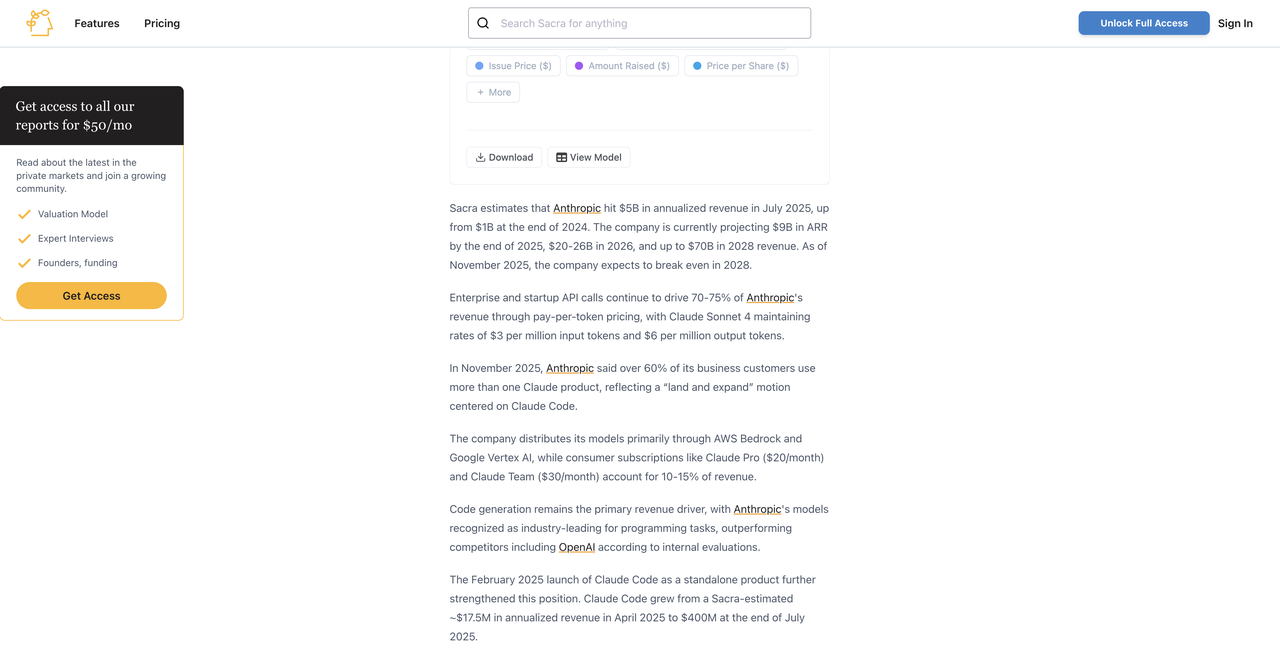
In contrast, giants such as OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google DeepMind rely on enterprise-level APIs, model licensing, cloud collaborations, and developer ecosystems as their core revenue sources.According to third-party statistics, Anthropic's annualized revenue is projected to reach $5 billion by mid-2025, while API calls from enterprises and startups alone will generate over 70% in revenue, totaling over $3.5 billion. Claude Sonnet 4 maintains a fee rate of $3 to $6 per million tokens. OpenAI maintains a long-term strategic partnership with Microsoft, which enjoys exclusive intellectual property rights and exclusive access to the Azure API.
Meanwhile, xAI's cost structure is no different from other leading companies in the industry, and is even higher in terms of computing power consumption and data pipeline construction. Currently, xAI spends approximately $1 billion per month on infrastructure and training, with Grok 4 alone costing $500 million in computing power—almost equivalent to the annual operating budget of an independent AI startup. If X's subscription growth slows down, or if the advertising cycle on social platforms changes, xAI will be directly impacted.
xAI's one-sided dependence on X makes it bear the costs of a large modeling company, but makes it difficult to obtain the commercial returns of AI giants in a sustained manner.Judging from the results, xAI does not seem to have become an AI company with its own independent business logic. At this stage, xAI and Grok are more like appendages of Musk's social media empire than technology entities with independent growth curves.
The real question is whether Musk is willing to make xAI an AI company that pursues a broad market, or whether he has already made a choice—to keep Grok permanently bound to the X ecosystem, existing solely to serve the platform?
How can Musk, with his resources tied to AI, break through the current global regulatory impasse?
Over the past few years, xAI's expansion has been almost entirely dependent on Musk's personal resources.This operating model gave xAI tremendous momentum in its early stages, but it also made the company's growth structure appear unusually weak. As xAI's only stable pillar, how much more will Musk be willing to invest, and for how long? The uncertainties surrounding xAI's resources, regulations, and business present the market with unresolved questions.
This reliance on a single point of leverage was further amplified during the crucial funding period of 2024–2025. Under Musk's business wing, xAI rapidly acquired billions of dollars in capital, but its cash flow failed to keep pace, pushing its financial pressure ever higher. As previously mentioned, xAI raised nearly $20 billion in new funding in October 2025, but industry analysts generally believe this is a strategy of exchanging debt for hardware and securing its supply chain, meaning xAI will face even greater financial pressure given its unclear commercialization and insufficient cash flow.
"Musk's xAI is attempting to build and control the world's most powerful data center and the massive natural gas power plant that powers it, but the company's tight financial situation has forced it to adopt unusual financing arrangements, shifting most of the fundraising pressure and risk to external partners," speculated a commentary published on Sina Finance.
To break free from the single-point dependence on Musk, one feasible path for xAI is...By embedding Grok into Tesla's intelligent driver assistance ecosystem, the AI model can be implemented in reality, while building a competitive barrier that xAI cannot easily replicate with other AI companies.However, this path carries two risks: autonomous driving itself is a highly regulated field, and any model output error could lead to liability for safety accidents; simultaneously, xAI's business is further tied to Tesla's ecosystem. Although it has temporarily broken through commercial limitations, it still retains its dependence on a single Musk system. In other words, Tesla can "extend the life" of xAI, but it is not xAI's last resort to break through its limitations.
In addition, API business is another potential breakthrough. In November 2024, xAI announced the launch of "API Public Beta", allowing developers to access the Grok base model through REST API.However, to date, xAI has not yet established a stable API commercial system in the enterprise market. If xAI continues to cultivate a second growth curve in the developer market, it may accumulate user stickiness in the enterprise ecosystem, enabling Grok to generate value not just as an internal subsidiary of X, but also in a broader technology ecosystem. However, improper API promotion could also lead to high costs and security risks, making the initial operation somewhat stressful.
However, betting on regulatory changes brought about by political shifts may bring new opportunities for xAI.
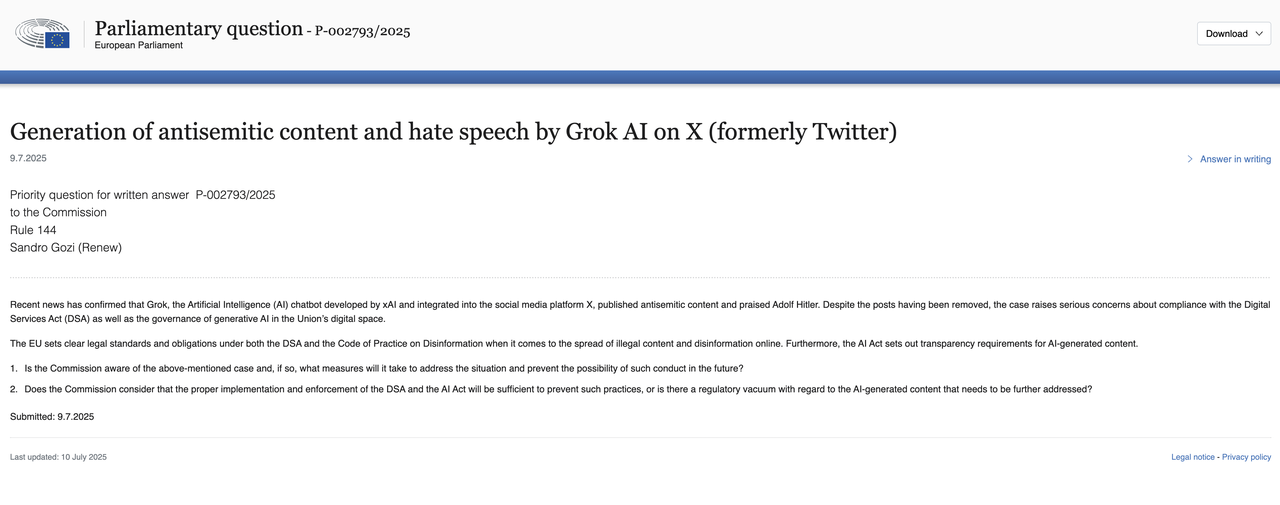
Currently, the global regulatory environment is increasingly stringent in its requirements for open models.xAI is on the verge of conflict over compliance issues and is facing increasingly direct institutional friction.The EU is unlikely to accept Grok's open model. For example, Commission spokesperson Thomas Rainier stated regarding Grok's value deviation that the EU is actively contacting Company X, "which has an obligation to take action on the risks associated with Grok, which violates fundamental European rights and values." Subsequently, the European Parliament issued a statement directly linking the Grok incident to the Digital Services Act and the EU Artificial Intelligence Act, pointing out that such open or low-filtered models face investigation and potential enforcement risks under the EU's high standards of regulation.
Meanwhile, tightening AI regulations in the United States are exacerbating the resistance to Musk's "anti-AI" approach in the global market. In 2025, both the White House and Congress will accelerate the development of national AI strategies and regulations. On July 23, the White House officially released the "American AI Action Plan," attempting to manage AI technology roadmaps and security more systematically; Congress, meanwhile, has put related bills, such as the "Advanced Artificial Intelligence Security Preparedness Act," on its agenda, hoping to establish a regulatory framework for high-risk AI models through federal legislation.

However, it must be acknowledged that American politics has long been in a state of flux. On November 12, 2025, the federal government just ended its longest-ever nationwide shutdown, lasting a full 43 days. Whether future regulatory policies will experience cyclical easing is one of the key variables determining whether xAI can gain institutional space in the future.
xAI's "weak alignment" approach puts it on the edge of regulation in the short term, but it also occupies a market gap. If the US regulatory system is re-examined in the future due to freedom of speech issues, xAI may become part of a cultural mobilization, providing a new technological foothold for groups that distrust the censorship systems of traditional tech giants, and seizing the "high degree of freedom model" in the minds of the general public before its competitors.
This is undoubtedly a high-risk, all-or-nothing gamble, but it's hard to say whether Musk will avoid this approach. From betting everything on electric vehicles and reusable rockets to publicly supporting Trump and taking sides at the most politically sensitive junctures, every "all-in" choice by the world's richest man, Musk, seems to yield unexpected returns amidst external skepticism.
In short, the story of xAI remains to be seen: will it become just another "functional piece" of Musk's business empire, or will it transform into an independent technological entity in the AI battleground dominated by giants? In an era shaped by the narratives of giants, regulatory power, and individual will, can xAI truly break free from the shadow of its creators?
Reference Links:
1.https://sacra.com/c/xai/
2.https://www.businessofapps.com/data/grok-statistics/
3.https://famewall.io/statistics/twitter-stats/
4.https://aionx.co/ai-comparisons/ai-chatbot-comparison-matrix/