Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
MMDeepResearch-Bench: A Benchmark for Multimodal Deep Research Agents
MMDeepResearch-Bench: A Benchmark for Multimodal Deep Research Agents
Abstract
Deep Research Agents (DRAs) generate citation-rich reports via multi-step search and synthesis, yet existing benchmarks mainly target text-only settings or short-form multimodal QA, missing end-to-end multimodal evidence use. We introduce MMDeepResearch-Bench (MMDR-Bench), a benchmark of 140 expert-crafted tasks across 21 domains, where each task provides an image-text bundle to evaluate multimodal understanding and citation-grounded report generation. Compared to prior setups, MMDR-Bench emphasizes report-style synthesis with explicit evidence use, where models must connect visual artifacts to sourced claims and maintain consistency across narrative, citations, and visual references. We further propose a unified, interpretable evaluation pipeline: Formula-LLM Adaptive Evaluation (FLAE) for report quality, Trustworthy Retrieval-Aligned Citation Evaluation (TRACE) for citation-grounded evidence alignment, and Multimodal Support-Aligned Integrity Check (MOSAIC) for text-visual integrity, each producing fine-grained signals that support error diagnosis beyond a single overall score. Experiments across 25 state-of-the-art models reveal systematic trade-offs between generation quality, citation discipline, and multimodal grounding, highlighting that strong prose alone does not guarantee faithful evidence use and that multimodal integrity remains a key bottleneck for deep research agents.
One-sentence Summary
Researchers from OSU, Amazon, UMich, and others introduce MMDeepResearch-Bench, a multimodal benchmark with 140 expert tasks evaluating citation-grounded report synthesis, and propose FLAE, TRACE, and MOSAIC for granular evaluation, revealing critical gaps in evidence fidelity and multimodal alignment for deep research agents.
Key Contributions
- We introduce MMDR-Bench, a first-of-its-kind benchmark with 140 expert-curated, multimodal tasks across 21 domains, designed to evaluate Deep Research Agents’ ability to synthesize long-form reports that integrate visual artifacts with citation-grounded claims, addressing the lack of end-to-end multimodal evaluation in prior work.
- We propose a three-component evaluation pipeline—FLAE for report quality, TRACE for citation alignment, and MOSAIC for text-visual consistency—each delivering interpretable, fine-grained signals to diagnose failures beyond aggregate scores, enabling precise assessment of multimodal grounding and evidence fidelity.
- Experiments across 25 state-of-the-art models reveal persistent trade-offs between prose quality, citation discipline, and multimodal integrity, with results showing that strong narrative output does not imply faithful evidence use, and visual grounding remains a critical bottleneck for current research agents.
Introduction
The authors leverage recent advances in large multimodal models to address the growing need for agents that can perform deep, evidence-based research across both text and visual data. Prior benchmarks either focus on text-only report generation or short-form multimodal QA, failing to evaluate how well systems integrate visual evidence into long-form, citation-rich synthesis — a critical gap for real-world research workflows. Their main contribution is MMDeepResearch-Bench (MMDR-Bench), a 140-task benchmark with expert-crafted image-text bundles spanning 21 domains, paired with a three-part evaluation framework: FLAE for report quality, TRACE for citation fidelity, and MOSAIC for text-visual consistency — together enabling granular diagnosis of agent failures beyond single scores.
Dataset
-
The authors define MMDR-Bench as a multimodal deep research benchmark consisting of 140 expert-crafted tasks across 21 domains, split into two regimes: Daily (40 tasks across 11 domains) and Research (100 tasks across 10 domains). Daily tasks use casual visuals like screenshots and UI captures, while Research tasks use structured visuals like charts and tables requiring deeper synthesis.
-
Each task is an image-text bundle: a textual query paired with a variable number of images that must be interpreted and cited in a generated report. Tasks are curated by domain experts and refined through checks for clarity, multimodal necessity (images must be essential), and evidence grounding (reports must be verifiable via citations).
-
The benchmark is multilingual, primarily in English and Chinese, with additional languages in the long tail. Tasks are annotated for difficulty (easy, hard, complex) and packaged with metadata including language and visual modality type.
-
The authors use the full 140-task set as an evaluation benchmark — not for training. No training split or mixture ratios are applied; the dataset serves as a fixed test suite to evaluate multimodal understanding and evidence-grounded report generation with citations. No cropping or preprocessing is mentioned beyond the expert curation and annotation steps.
Method
The evaluation framework for long-form deep research reports is structured around three primary modules: FLAE (Formula-LLM Adaptive Evaluation), TRACE (Trustworthy Retrieval-Aligned Citation Evaluation), and MOSAIC (Multimodal Support-Aligned Integrity Check). These modules operate in parallel on the generated report, each assessing distinct aspects of quality, and are integrated through a gating mechanism to produce a final score. The overall pipeline begins with a multimodal deep research report generated by an agent, which is then processed by each of the three evaluators. The outputs from FLAE, TRACE, and MOSAIC are passed through a multimodal gate that determines whether the report meets a minimum threshold for each module, with the final score being computed only if all gates are activated.
FLAE evaluates the report on three task-agnostic dimensions: Readability (READ.), Insightfulness (INSH.), and Structural Completeness (STRU.). This evaluation is conducted through a dual-channel approach. The formula-based channel computes per-dimension scores using a set of lightweight, directly observable text features ϕ(R), such as lexical diversity, sentence-length distribution, and compliance indicators like the presence of a references section. These features are mapped to scores via fixed, auditable transforms defined by linear models with sigmoid activation and clipping, ensuring reproducibility. The LLM judge channel uses a calibrated prompt to generate per-dimension scores based on the task and report. To combine these channels, FLAE employs an adaptive fusion mechanism. A judge LLM calculates a fusion coefficient α(t,R) that controls the mix between the formula and judge scores, with the coefficient constrained to depend only on model-agnostic signals like report length and formatting compliance. This adaptive fusion is designed to mitigate bias and ensure the final score is a balanced combination of objective metrics and expert judgment. The final FLAE score is a weighted sum of the fused per-dimension scores, where the weights are task-adaptive and determined by a separate judge LLM prompt.
TRACE assesses the report's grounding in cited sources and its faithfulness to the task. It first parses the report to extract claim-URL pairs, mapping each citation to its corresponding source. For accessible sources, a judge LLM verifies the support for each claim, accounting for evidence consistency, coverage, and textual fidelity. This process yields three citation-fidelity metrics: Consistency (Con.), Coverage (Cov.), and Textual Fidelity (FID.). Additionally, TRACE includes a strict visual evidence fidelity (VEF.) check to ensure the report correctly interprets and answers the task's visual requirements. The VEF. score is a discrete value from 0 to 10, and a PASS/FAIL verdict is enforced by a fixed threshold of 6, making this component auditable and consistent across different judge models. The final TRACE score is a weighted combination of the VEF. score and the other three metrics, with the weights being task-adaptive.
MOSAIC evaluates the integrity of the report's multimodal content by verifying that image-referenced statements are faithful to the underlying visuals. It begins by parsing the report to extract multimodal items (MM-items), which include text that references images and the images themselves. These items are then routed to a type-specific evaluator based on their visual modality—photo, data chart, or diagram—using a lightweight router. Each item is scored on three dimensions: Visual-Semantic Alignment (SEM.), Visual Data Interpretation Accuracy (ACC.), and Complex Visual Question Answering Quality (vQA). The item-level score is computed by a weighted aggregation of these dimension scores. The final MOSAIC score is derived from the item-level scores, and the module's activation is gated by the performance of the other two evaluators.
Experiment
- Evaluated multimodal Deep Research agents via MMDR-Bench, combining FLAE (20%), TRACE (50%), and MOSAIC (30%) with gated activation; Gemini-2.5-Pro served as judge LLM.
- Gemini Deep Research ranked first overall, excelling in evidence quality (TRACE) and maintaining strong multimodal alignment (MOSAIC); Gemini 3 Pro (Preview) led non-agent web-enabled models.
- Vision improves performance only when reliably grounded; adding vision to Qwen 3 models increased fine-grained extraction errors (e.g., misreading numerals, labels), revealing prompt-fidelity bottlenecks.
- Multimodal alignment and citation grounding can diverge: Gemini Deep Research improved evidence coverage but saw increased entity misattribution during multi-step synthesis.
- Tool use amplifies strong backbones but doesn’t replace them; Tongyi Deep Research (30B) underperformed larger models, while Gemini Deep Research (Gemini 3 Pro) combined high coverage and overall strength.
- On Research tasks, Gemini Deep Research and Gemini 3 Flash led broadly; GPT-5.2 excelled in Computer & Data Science; Qwen 3 VL dominated Environment & Energy via chart/diagram grounding.
- Human evaluation (12 experts, 140 tasks) confirmed evaluator alignment: full system outperformed vanilla judges; VEF. and MOSAIC improved human consistency (PAR/OPC metrics).
- Cross-judge tests (GPT-5.2 vs Gemini-2.5-Pro) showed stable overall scores (±0.30 points) despite per-module variance; MOSAIC remained highly consistent across judges.
- VEF. uses strict task-specific visual ground truth (PASS/FAIL at score ≥6); identity errors force immediate FAIL; pass-rate reported as % over tasks (e.g., 38.57% = 38.57% pass rate).
- Failure analysis revealed: vision-enabled models increase DTE (detail extraction errors); agentic systems increase EMI (entity misidentification) due to drift across multi-step synthesis.
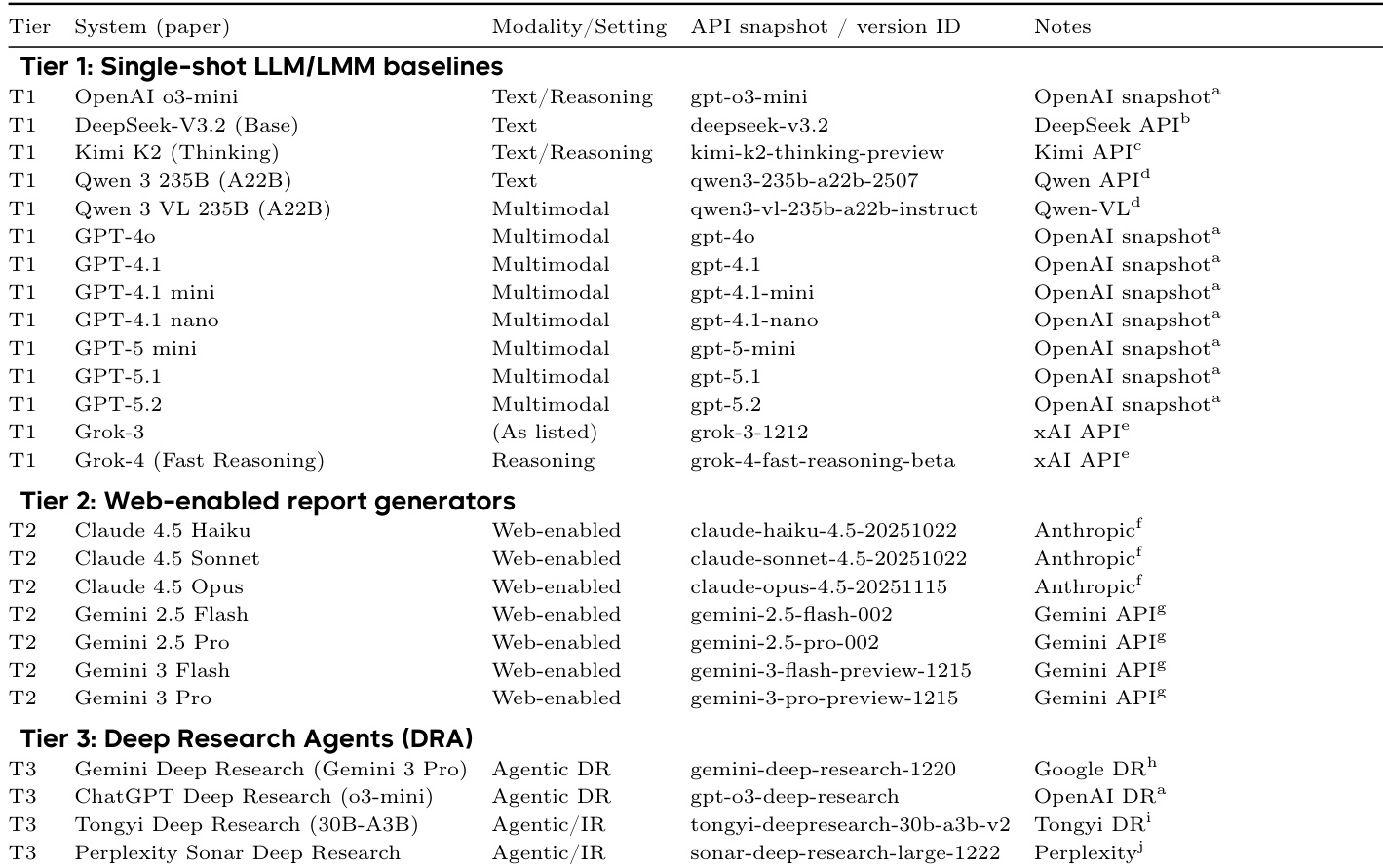
The authors use a multimodal evaluation framework to assess Deep Research agents, with results showing that Gemini-2.5-Pro achieves higher scores than GPT-5.2 across most metrics, particularly in AVG FLAE and AVG MMDR with VEF. inclusion. GPT-5.2 performs better in AVG TRACE and AVG MMDR without VEF., indicating stronger evidence quality but lower visual fidelity, while Gemini-2.5-Pro maintains more consistent multimodal alignment and overall performance.
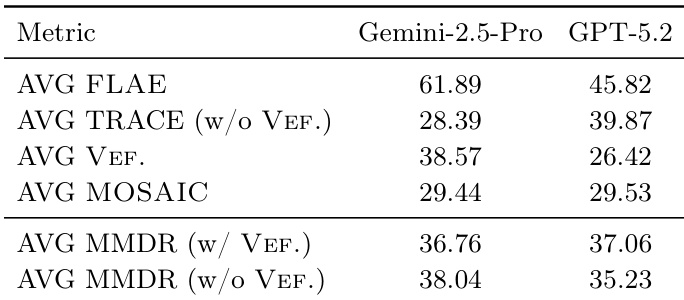
The authors use a normalized scoring system for visual items in the MOSAIC evaluation, where the score for each visual type is computed as a weighted combination of a feature score and a quality metric. For datacharts and ocrcharts, the score is based on accuracy and visual quality, while for photos it combines semantic and visual quality, and for diagrams it balances visual quality with a binary indicator of structural correctness.
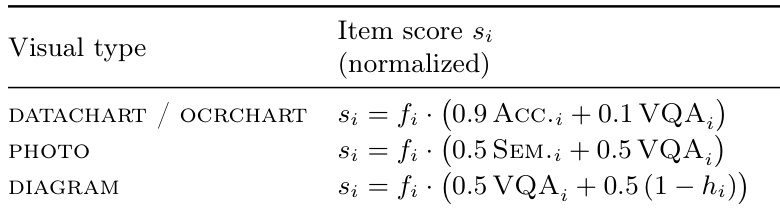
The authors evaluate the alignment between their automated evaluator and expert judgments by comparing pairwise preferences and score correlations across 140 tasks. Results show that the full evaluator, which uses a fusion coefficient derived from judge outputs, achieves higher agreement with experts (PAR 73.5, OPC 96.4) than a formula-only or judge-only baseline, indicating that the fusion approach better captures human preferences.

The authors use a human consistency check to evaluate alignment between their automated evaluator and expert judgments on multimodal reports. Results show that the full MMDR-Bench-Eval system achieves higher pairwise agreement (PAR) and score correlation (OPC) with experts compared to a vanilla prompt-based judge, indicating improved human-aligned scoring. Removing MOSAIC reduces performance, while omitting VEF. has a smaller impact, suggesting both components contribute to more accurate evaluation.
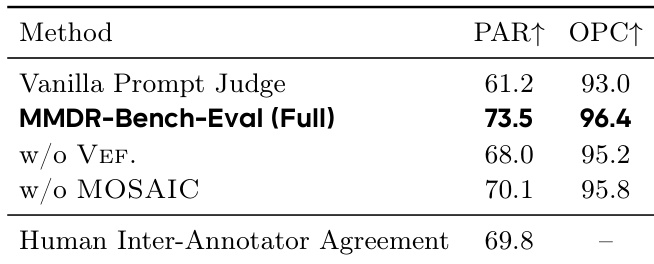
The authors use a three-tier evaluation framework to assess multimodal deep research agents, with Tier 1 consisting of single-shot LLM/LMM baselines, Tier 2 of web-enabled report generators, and Tier 3 of dedicated deep research agents. Results show that Gemini Deep Research (Gemini 3 Pro) achieves the highest overall score, driven by strong evidence quality and multimodal alignment, while also demonstrating that vision and tool use provide benefits only when reliable and well-integrated into the system.